CONTEXT:
DART , a new mission was launched by NASA on 24th November,2021 to test the technology for defending Earth against potential asteroid or comet hazard. It was successfully launched from the Vandenberg US Space Force Base. It carried aboard SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket.
NASA tweeted that about 55 minutes into its flight, the spacecraft separated from the Falcon 9 second stage, and will soon begin to orient itself toward the Sun.
What is this mission?
- It is the NASA’s first planetary defense test mission.
- The main aim of the mission is to test the new technology that would allow a spacecraft to crash into an asteroid and change its course.
- DART will be the first demonstration of the kinetic impactor technique to change the motion of an asteroid in space. It will show that a spacecraft can autonomously navigate to target asteroid and intentionally collide with it. This method of deflection is called Kinetic impact.
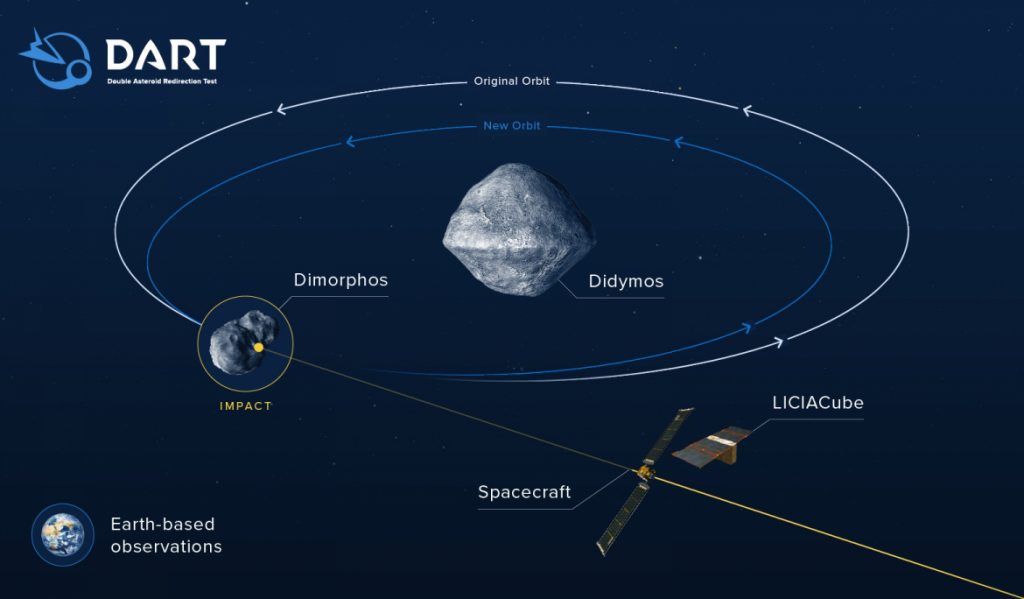
- DART will impact an asteroid which is presently not a threat to the Earth. The objective is to slightly change its motion so as to accurately measure using ground based telescopes.
Which Asteroid is the target?
- The target of the spacecraft is a small moonlet called DIMORPHOS.
- Dimorphos orbits a larger asteroid named DIDYMOS.
Note: The asteroid and the moonlet do not pose any threat to Earth and the mission is to test the new technology to be prepared in case an asteroid heads towards Earth in the future. The collision is expected to take place between September 26 and October 1, 2022.
Why DIMORPHOS?
DART Mission Coordination Lead and Planetary Scientist explained that Didymos is a perfect system for the test mission as it is an eclipsing binary .
- Binary means it has a moonlet DIMORPHOS that regularly orbits the asteroid DIDYMOS and it can be observed when it passes in front of the main asteroid.
- Earth-based telescopes can study this variation in brightness to understand how long it takes Dimorphos to orbit Didymos.
- The timing for the DART impact is when the Didymos system is closest to the Earth. So the telescopes can really make the foremost precise measurement possible.
ABOUT THE SPACECRAFT:
DART is a low-cost spacecraft, weighing around 610 kg at launch and 550 kg during impact.
It has two solar arrays and uses hydrazine propellant for maneuvering the spacecraft.
It also carries about 10 kg of xenon which will be used to demonstrate the agency’s new thrusters called NASA Evolutionary Xenon Thruster–Commercial (NEXT-C) in space.
DART’s single instrument, the Didymos Reconnaissance and Asteroid Camera for Optical navigation (DRACO), will turn on a week from now and provide first images from the spacecraft.
DART also will carry a little satellite or CubeSat named LICIACube (Light Italian CubeSat for Imaging of Asteroids). It will be deployed ten days before the impact on Dimorphos.
LICIACube is predicted to capture images of the impact and therefore the impact crater formed as a results of the collision. It also can capture images of any cloud formed during the impact.